Steampipe provides a trio of mods that check your deployed AWS, Azure, and GCP infrastructure for compliance with frameworks such as CIS, HIPAA, NIST 800, and SOC 2.
If you're using Terraform to define that infrastructure, there's now a companion trio of mods that run compliance controls -- again for AWS, Azure, and GCP -- that check that your defined infrastructure complies with best practices.
The mods that check deployed infrastructure use cloud APIs, provided by the AWS, Azure, and GCP plugins, to query your environments in realtime. The mods that check Terraform-defined infrastructure rely on a single plugin, Terraform, which turns the HCL code in your .tf files into data that you can query with SQL.
To explore how these Terraform compliance mods work, we'll use the examples from https://github.com/futurice/terraform-examples. Here's the initial setup.
Running a S3 control on Terraform files in a directory
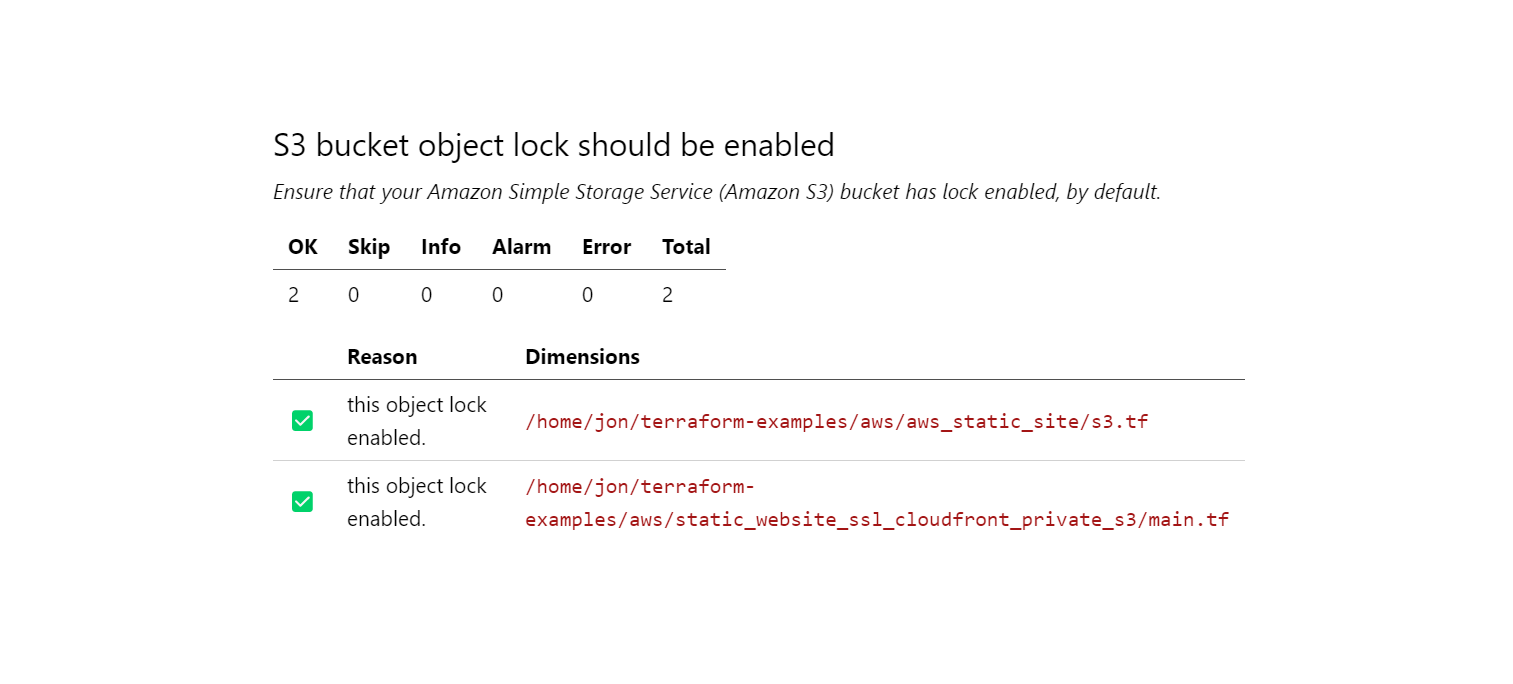
The terraform_aws_compliance mod defines 39 benchmarks, based on 153 controls and 153 named queries. First, we'll run a single control, S3 bucket object lock should be enabled, on the examples in one subdirectory of the repo.
By default the Terraform plugin looks for .tf files in the current directory. The --workspace-chdir argument points to the directory into which we cloned the terraform_aws_compliance mod that defines the s3_bucket_object_lock_enabled control.
Here's the Markdown output.
s3.tf fails to comply with the policy enforced by the control. How does Steampipe define that policy? Here's the control.
It refers to this named query.
Steampipe expects .tf files that provision S3 buckets to include an argument like this.
We'll fix the problem by adding the argument to the aws_s3_bucket resource, then repeat the check.
All good now!
Querying HCL with SQL
The Terraform compliance mods use the Terraform plugin to query .tf files. These mods provide a rich catalog of named queries. The mods run those queries for you, but you can also run them directly in Steampipe.
For our next examples, let's include all the subdirectories of the repo. To do that, we'll edit ~/.steampipe/config/terraform.spc and set paths = ["~/terraform-examples/**/*.tf"] to match all Terraform files in ~/terraform-examples and its subdirectories.
The Terraform plugin defines these tables.
At each of those links you'll find yet more sample queries. And you can also easily write your own queries. Here's a query that extracts assume_role_policy statements from aws_iam_role resources.
Here's one that counts resources by type.
Querying deployed and defined infrastructure
For deployed infrastructure, Steampipe's compliance mods support these frameworks with a combined total of 1,120 named queries and 770 controls:
-
AWS: Audit Manager Control Tower, AWS Foundational Security Best Practices, CIS, GDPR, HIPAA, NIST 800-53, NIST CSF, PCI DSS, RBI Cyber Security Framework and SOC 2.
-
Azure: CIS, HIPAA HITRUST and NIST
-
GCP: CIS, Forseti Security and CFT Scorecard
-
Kubernetes: NSA and CISA Kubernetes Hardening Guidance
For defined infrastructure, the new set of compliance mods delivers an additional 359 queries and 359 controls. We think the ability to query both deployed and defined resources is unique and powerful. We hope you'll give it a try, and look forward to hearing your feedback on Twitter or Slack.